Boolean Algebra in Nutshell
There are only two Boolean values:
- True (1, yes, on)
- False (0, no, off)
Basic Operators
AND Operator (∧)
The AND operator returns True only when both inputs are True.
Truth Table:
| A | B | A AND B |
|---|---|---|
| False | False | False |
| False | True | False |
| True | False | False |
| True | True | True |
OR Operator (∨)
The OR operator returns True when at least one input is True.
Truth Table:
| A | B | A OR B |
|---|---|---|
| False | False | False |
| False | True | True |
| True | False | True |
| True | True | True |
NOT Operator (¬)
The NOT operator flips the value - True becomes False, False becomes True.
Truth Table:
| A | NOT A |
|---|---|
| False | True |
| True | False |
Combining Operators
You can combine operators to create complex logical expressions.
Operator Precedence (Order of Operations)
1. NOT (highest priority)
2. AND
3. OR (lowest priority)
Example: A OR B AND C
- First do: B AND C
- Then do: A OR (result)
Use parentheses to be clear: (A OR B) AND C
Venn Diagrams
Write an expression to represent the outlined part of the Venn diagram shown.
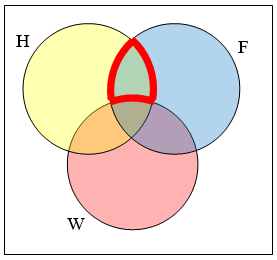
Image from Book Title by David Lippman, Pierce College. Licensed under CC BY-SA. View original
A survey asks 200 people "What beverage do you drink in the morning?", and offers these choices:
- Tea only
- Coffee only
- Both coffee and tea
Suppose 20 report tea only, 80 report coffee only, 40 report both.
Questions:
a) How many people drink tea in the morning?
b) How many people drink neither tea nor coffee?
Fifty students were surveyed and asked if they were taking a social science (SS), humanities (HM) or a natural science (NS) course the next quarter.
- 21 were taking a SS course
- 26 were taking a HM course
- 19 were taking a NS course
- 9 were taking SS and HM
- 7 were taking SS and NS
- 10 were taking HM and NS
- 3 were taking all three
- 7 were taking none
Question: How many students are taking only a SS course?
Problems adapted from David Lippman, Pierce College. Licensed under CC BY-SA.